Project SEO Blog 11:
EWT Blogs k00121609 2017
Project SEO
SEO Website Project url: https://k00121609.github.io//SEOEWT
Git-hub repository: SEOProject.
This Blog url name: creativemultimediaprogrammingsb.blogspot.com
__________________________________________________________
April
1. Structured data mark-up helper (in WMT Other
Resources section):
Here I clicked on the article link for this topic. Then, logged in
to Google and was brought to this page on the topic:
Structured
data make-up helper actions:
1. Data Highlighter:
“Note that Data
Highlighter can only access pages that have been crawled by Google recently. If
Google hasn't crawled or can't crawl some of your pages, such as pages behind
sign-in forms, you can't use Data Highlighter for those pages.”
·
As I make the changes there is a window to the
right of screen that shows how Google is applying the changes I am making to
the website for structured data.
1. Metadata:
Important keywords are first in the sequence: Creative Multimedia, LIT, Awards,
Read Review
Look at any Creative Multimedia/LIT surveys for: ratings/other
data
I have
subscribed to this “Search Engine Watch” newsletter on latest search trends:
Adding the
metadata to my HTML page:
<meta name= “description” content= “Here is a precise
description of my awesome webpage.”>
</head>
1. Search Traffic Queries:
1. Internal Links:
1. GOOGLE INDEX: Index status:
1. Content Keywords:
1. Sitemaps:
1. Other Resources:
1.
Author Stats:
1.
Instant Previews:
1.
Bing Webmaster Tools: (Check
this one)
Project SEO
SEO Website Project url: https://k00121609.github.io//SEOEWT
Git-hub repository: SEOProject.
This Blog url name: creativemultimediaprogrammingsb.blogspot.com
__________________________________________________________
April
1. Structured data mark-up helper (in WMT Other
Resources section):
“You can use the
helper to embed structured data right onto webpages, as the tool provides
microdata annotations you copy into the page’s HTML. You can then use this
information to tag similar pages on your site.”
Here I clicked on the article link for this topic. Then, logged in
to Google and was brought to this page on the topic:
Structured
data make-up helper actions:
a.
Articles: use article tag
b.
Local Businesses: add Enterprise centre at LIT
c.
Restaurants: add ‘Insomnia’ at LIT
d.
TV Episodes with Ratings: look to see if
there’s any LIT ratings on their news page
e.
Book Reviews: check if any publications in
Creative Multimedia
f.
Software Applications: look at the Creative
Multimedia recent competition winners
g.
Events: highlight my academic calendar of
events in the website
h.
Products: products derived from student fyp
projects and similar
i.
TV Episodes: in the LIT news section of
website
The process for this is to: enter my url, tag data and view html.
1. Data Highlighter:
This is stated as an
alternative to “Web-Master Mark-up.” Using this tool helps Google understand
the websites data. The end-product is that Google can “present data more
attractively and in new ways, in search results.”
First, Google has updated their Data Highlighter to now cover eight
types of structured data, which allows webmasters to easily tag key fields on
their sites for the applicable structured data. The tool now includes the
following types:
§ Events
§ Products
§ Local businesses
§ Articles
§ Software applications
§ Movies
§ Restaurants
§ TV episodes
To use the tool, you need to login to Webmaster Tools, choose your site
and then click “Optimization”, then “Data Highlighter”. It gives you the option
to tag a single page or multiple pages, verify the tags, and then “publish” it
to Google. The process will take webmasters about 5 minutes for single pages,
and 15 minutes of a series of similar pages.
“If your site contains
event listings you can use Data Highlighter to tag data (name, location,
date, and so on) for the events on your site. The next time Google crawls your
site, the event data will be available for rich snippets on search results
pages:”
“Note that Data
Highlighter can only access pages that have been crawled by Google recently. If
Google hasn't crawled or can't crawl some of your pages, such as pages behind
sign-in forms, you can't use Data Highlighter for those pages.”
The advice is to
create “page sets” that follow a certain structural pattern. I have designed my
website so that it is one long scrolling page. Therefore, all the information
is one set. From this I have created out-links for more information on the
topics included.
Procedure:
·
There is no need to change websites HTML
·
Just highlight data items with the mouse and
select their type similar to this next image:
·
As I make the changes there is a window to the
right of screen that shows how Google is applying the changes I am making to
the website for structured data.
·
When complete I click ‘Publish,’ and Google
will apply these patterns to my site.
·
Google can then show this structured data in
my snippets.
1. Metadata:
Usefulness
of metadata:
·
For search engines and website visitors
·
HTML attributes that provide concise
explanations of the contents of web pages
·
Commonly used on search engine results pages
(SERP’s) to display preview snippets for a given page
·
Treat it as an advertisement for my website
Best
metadata actions for my website:
Important keywords are first in the sequence: Creative Multimedia, LIT, Awards, Read Review
Important keywords are first in the sequence: Creative Multimedia, LIT, Awards, Read Review
-Update my news section of the website with the recent Creative
Multimedia Student winners
Emotive sentences: Creative Multimedia award success sees….
Written in a natural, clear, readable way- so they will not appear
as spam: natural sentences
Keep it short and concise-no longer than 135-160 characters long
(though Google has recently been testing longer snippets)
The following is an example of metadata using “rich snippets” of star
ratings:
Look at any Creative Multimedia/LIT surveys for: ratings/other
data
I have
subscribed to this “Search Engine Watch” newsletter on latest search trends:
Adding the
metadata to my HTML page:
<head>
<meta name= “description” content= “Here is a precise description of my awesome webpage.”>
</head>
<meta name= “description” content= “Here is a precise description of my awesome webpage.”>
</head>
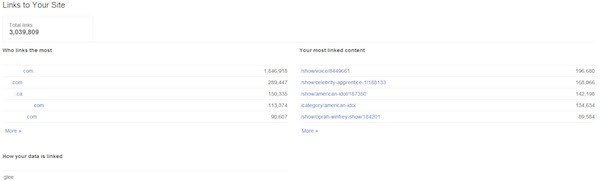
1. Search Traffic Queries:
“This section identifies the domains
that link to you the most, along with your most-linked-to content. While you most likely
won’t see every link that Google’s found for your site, you will see more than
if you went to google.com and performed a search for “link:yoursite.com.”
1. Internal Links:
“Here you can see the top 1,000 pages
on your site sorted by the number of internal links to those pages. If you have
a small number of pages on your site, you can reverse the sort order by
clicking on the Links header.”
“Any pages that show zero internal
links have been orphaned and should either be linked to from somewhere on your
site, or redirected to an appropriate page if they’re old legacy pages.”
1. GOOGLE INDEX: Index status:
“The Index Status allows
you to track the status of your site within the Google index. How many pages
are they showing as being indexed? Are there any worrying trends? Have you
accidentally blocked large sections of your site from Googlebot? This is a
great place to get the answers to those questions and more.”
1. Content Keywords:
Most commonly found keywords by the
Google crawler as it navigated through my website. (Check for unexpected words
as indications of website being hacked)
1. Fetch as Google:
Here I can view my pages as Google
sees them. They return the HTTP response, date and time and HTML code
(including the first 100kb of visible text on the page. (If the page looks as I
expect it to I can submit it to the index).
2. Blocked URL’s:
“This section is the place to test out
your current robots.txt against any pages on your site to verify whether they
can be crawled or not. You can also test out modifications to your robots.txt
to see whether they’d work as you anticipate against various pages on your
site.”
1. Sitemaps:
The page shows you the sitemaps that you’ve submitted, the
number of pages they found in each, and the number of those pages that
they’ve indexed.
1. Other Resources:
This section contains links to tools that are outside of GWT,
but are of interest to webmasters, such as the Structured Data Testing tool,
which enables webmasters to test their schema implementations, the Structured Data Markup Helper, and others.
1.
Author Stats:
With the big push to tie up by-lines to Google+ accounts,
this tool allows you to see data for pages which you are the author for, so
you’d need to be logged into an account in GWT that you’ve previously set up as
an author.
1.
Instant Previews:
This tool allows you to see how your site looks using
Google’s Instant Preview feature (the view of your site that can be seen in the
search results when you mouse over the double arrows that show up next to a
result).
1.
Bing Webmaster Tools: (Check
this one)
Now that you’re up to
speed on Google Webmaster Tools, don’t forget about another search engine
offering a free toolset to webmasters that you should also be using: Bing. See Bing Webmaster Tools: An Overview for a complete guide.














Comments
Post a Comment